|
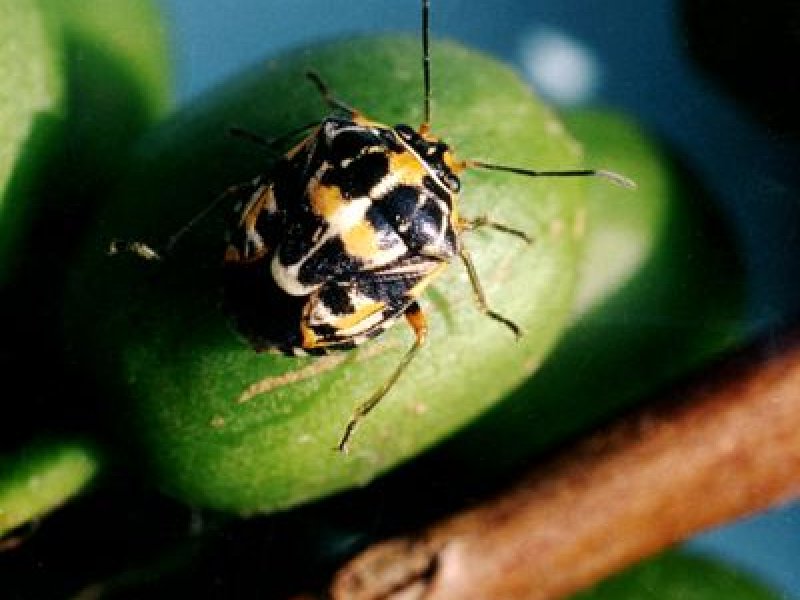
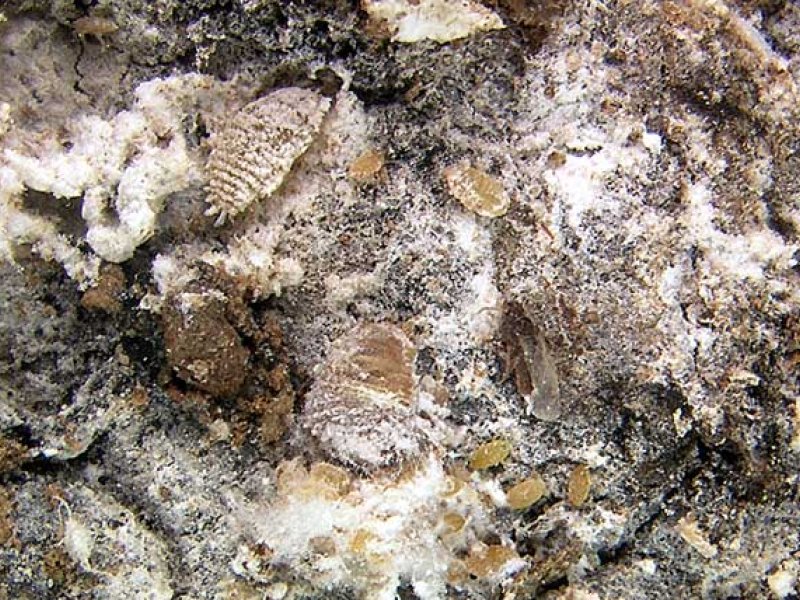
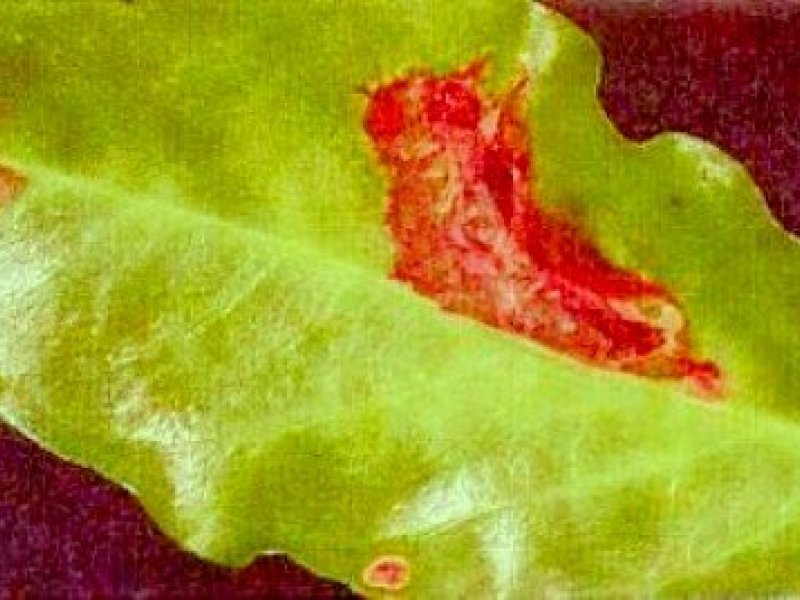
Antestia bugs (Antestiopsis spp) Antestia bugs are major pest of Arabica coffee in East African countries. The adult bug is shield-shaped, about 6 to 8 mm long and strikingly coloured dark brown with orange and white markings. They hide in berry or flower clusters. Females lay eggs in groups of about 12 on the underside of leaves. Newly hatched nymphs are about 1 mm long. Nymphs resemble the adults in colour but have a more rounded shape and lack functional wings.
Both adults and nymphs cause severe damage to green berries by feeding and indirectly by the transmission of a fungus (Nematospora coryli), which causes rotting of beans. The bug also attacks flower buds and shoots causing blackening of flower buds with no flower/fruit set. Attacked branches grow side shoots (fan branching). No visible surface marks / scars or wounds on berry are noticeable until seen on drying beds as "zebra" beans. "Zebra" beans produce poor quality coffee and are possible avenues for fungal infection. Antestia bugs can live on shrubs belonging to the same family as coffee (Rubiaceae family).
|
|
|
What to do:
|
|
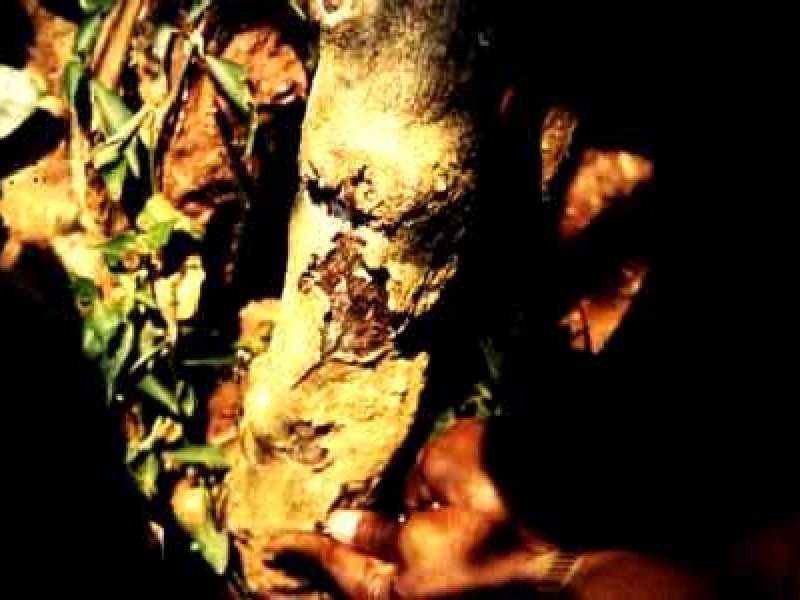
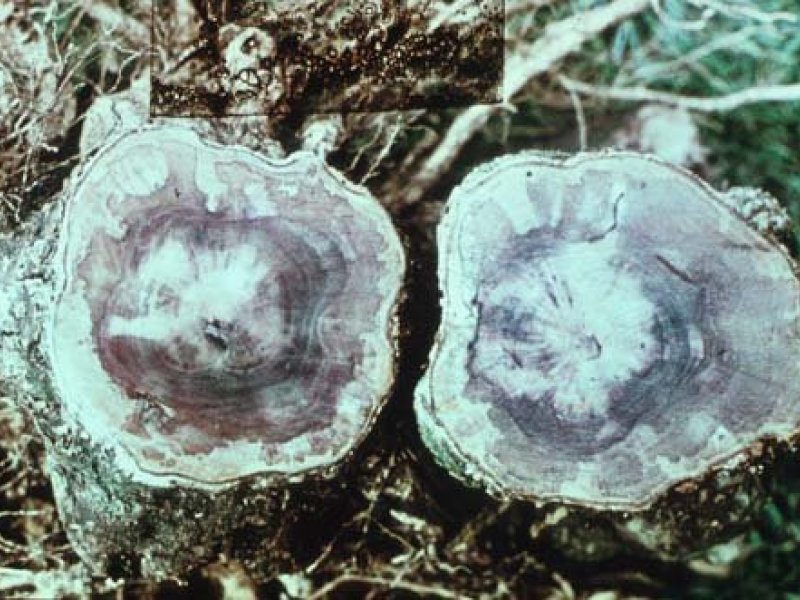
Armillaria root rot (Armillaria heimii) Symptoms include wilting of leaves, death of verticals and subsequent death of affected trees. The root system of affected trees shows a white growth (mycelial) of the fungus beneath the bark. In advanced stage of the disease the wood of the affected tree is decomposed into a white, wet mass with characteristic black zone lines running through the wood tissue. Vertical cracks may occur at the base of the stem at this stage. Initial infection in coffee plantings usually can be traced to shade trees or woody debris (stumps or old roots of shade trees) left in the ground when land is cleared before coffee planting.
|
|
|
What to do:
|
|
Bacterial blight of coffee (Pseudomonas syringae pv. garcae) Bacterial blight of coffee (BBC) is confined to a few coffee growing areas in Kenya (Solai in Nakuru District and around Mt. Elgon). Recently a few cases have been reported in the East of Rift Valley.
This bacterium is favoured by cool wet weather. Lesions appear on leaves with water soaked margins at start of infection. Leaves eventually dry up and roll inwards turning brown. Dead and dried leaves do not shed but remain attached to the plant. Symptoms occur on secondary or tertiary branches and in severe cases the heads may be affected. On twigs the terminal bud is attacked. Infection then extends downwards, resulting in dieback. Flowers and pin-heads shrivel and turn black.
The initial symptom is the blackening of a node often accompanied by blackening of the petiole and basal part of the leaf. This leads to death of the branch above the node and leaves on the branch turn brown and eventually necrotic (burnt). Severely affected trees appear scorched as if by fire. The bacterium persists on leaves, berries and on green and matured bark. During cool, wet weather, the bacterium multiplies and initiates an epidemic. The entire crop may be lost.
|
|
|
What to do:
|
|
Capsid bug (Lamprocapsidea (Lygus) coffeae) The capsid bug is a serious pest in all areas. The adult bug is green or brownish and about 0.7-0.8 mm long, and has a sharp downward bent in its wings, which is highly characteristic. Females insert eggs into flower buds, and thus eggs are not visible. Nymphs are pale green and pear shaped. Wing buds are visible on older nymphs. Both adults and nymphs feed on flower buds, but when they are not present they would feed on any soft green part of the coffee bush. As a result of feeding flower buds blacken due to death of stamens and petals. The style however remains healthy and usually takes a club shaped appearance with pale green shaft and black head. Damaged flowers do not set fruit. This bug is frequently considered beneficial on unshaded coffee at lower altitudes since the pruning effect of the damage caused by this bug reduces the tendency to overbear.
|
|
|
What to do:
|
|
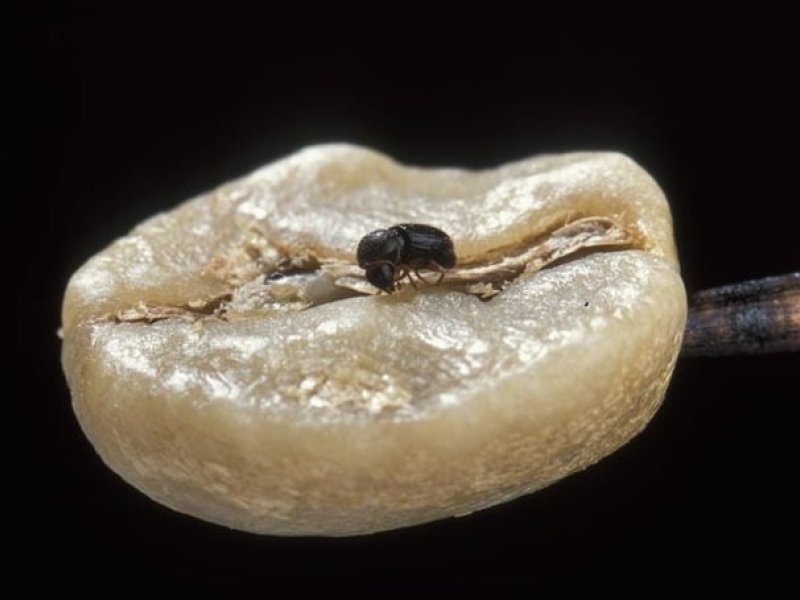
Coffee berry borer (Hypothenemus hampei) It is the most serious pest of coffee in many of the major coffee-producing countries. Crop losses caused by this pest can be severe, ranging from 50 to 100% of berries attacked if the pest is not controlled. The adult is a tiny (about 1.5 to 2.5 mm long), cylindrical blackish beetle. The females (1.4 to 1.6 mm) penetrate into mature green or red berries, usually from the tip and lay eggs within the beans. Female beetles fly from tree to tree to lay eggs. Once the eggs hatch, the larvae feed on the beans, rendering them unsuitable for commerce or greatly lowering their quality. The white, legless grubs have a brown head. They feed by tunnelling in the tissues of the beans destroying them. Pupation takes place in the berry. Symptoms of attack are one or more small round holes near the apex of large green or ripe berries. The damaged beans, which have a distinct blue-green staining contain up to 20 grubs. Female beetles also attack young berries. Coffee berry borer damage predisposes the coffee bean to fungal infection and hence contamination with mycotoxins (food poison). Reasons for the infestation with coffee berry borer can be: the plantation is at a too low altitude, too much shade or that there are abandoned or infested plantations nearby. Infestations are carried over between peaks of fruiting by breeding in over-ripe berries left on the tree or fallen to the ground.
|
|
|
What to do:
|
|
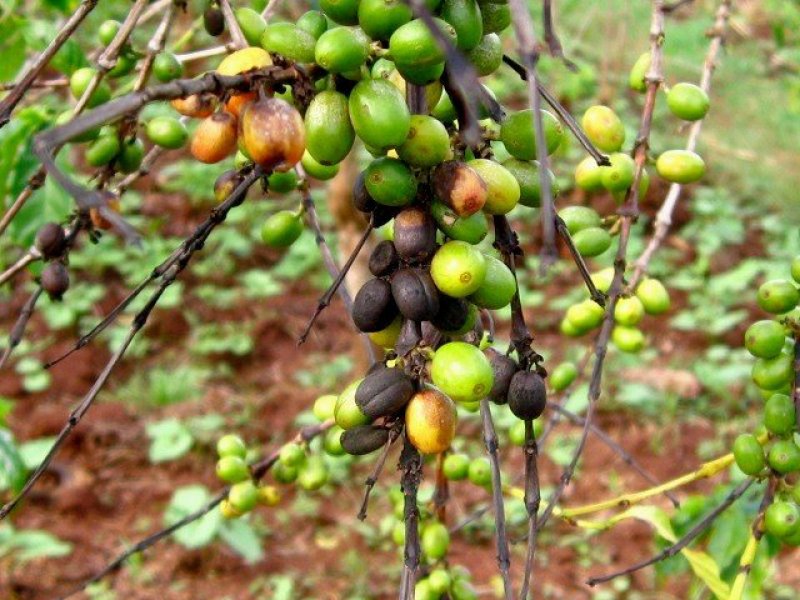
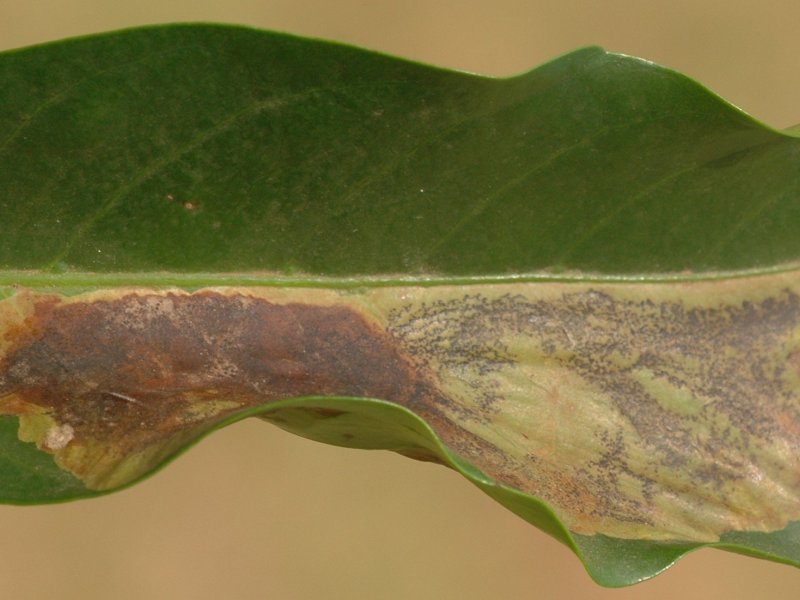
The coffee berry disease (Colletotrichum kahawae) Colletotrichum kahawae of Arabica coffee only occurs in Africa, and causes major damage in East Africa and Cameroon. Other names of this disease are "coffee berry anthracnose" and "brown blight of coffee". The characteristic symptom is a progressive blackening of young, expanding coffee berries. This begins as small water-soaked lesions. They rapidly become dark and sunken. As they grow they cause the whole berry to rot. Under humid conditions, pink spore masses become visible on the surface of the lesion. Berries often drop from the branch at an early stage of the disease. This is a characteristic feature of coffee berry disease. Lesions may also occur on young berry stalks, causing them to be shed before lesions are visible on the berry itself. The disease also affects ripening berries causing a 'brown blight' phase. This phase is characterised by typical dark, sunken lesions that envelop the red berry. The coffee berry disease may also infect flowers under very wet conditions, and causes brown lesions on petals. This disease does not kill trees, but crop losses can be more than 80%. Spore dispersal within the tree is by rain splash. Disease spread from tree to tree and from farm to farm is by coffee pickers, birds or infected seedlings. Wet conditions and temperatures between 15 and 27.7° C favour disease development. |
|
|
What to do:
|
|
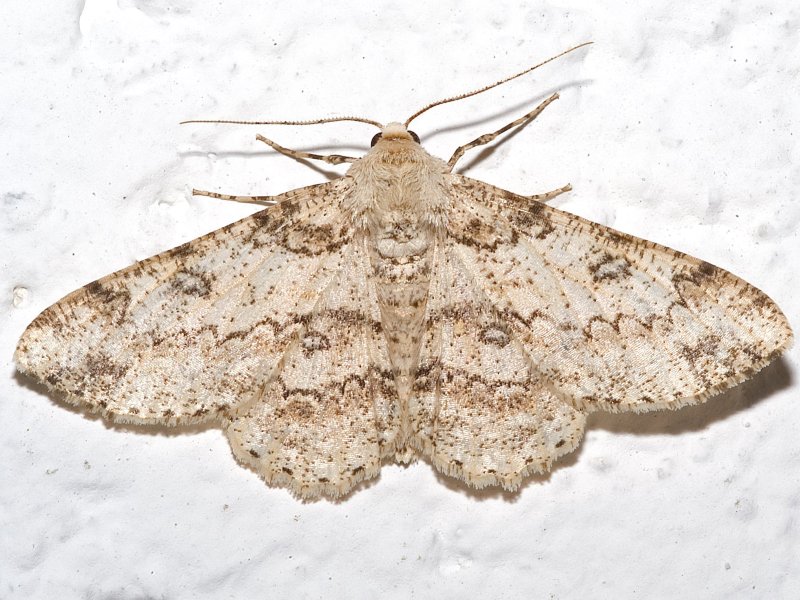
Coffee berry moth (Prophantis smaragdina) The adult is a small golden brown moth with a wingspan of about 1.3 mm. The female moth lays scale-like eggs singly on or near green berries. The caterpillar is reddish to pink in colour with dark markings on the back, and measures 13 mm when fully grown. Caterpillars bore into green, half-grown berries, starting near the stalk and hollow them out. One caterpillar usually attacks several berries in 1 cluster. Attacked berries turn brown to black. When 1 bean has been eaten, it leaves the berries and wanders over the cluster of berries joining them with threads of silk before boring into a second berry. Flower buds and the tip of suckers may also be attacked. Caterpillars pupate on the ground between dry leaves. Occasionally severe attacks occur at low altitudes. Frequently slight damage by the berry moth is considered beneficial since it has the effect of thinning out overbearing branches.
|
|
|
What to do:
|
|
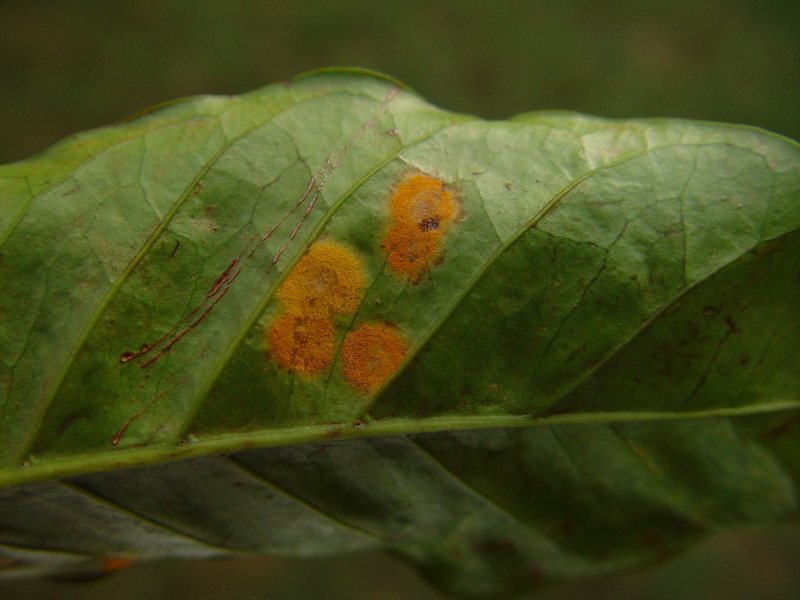
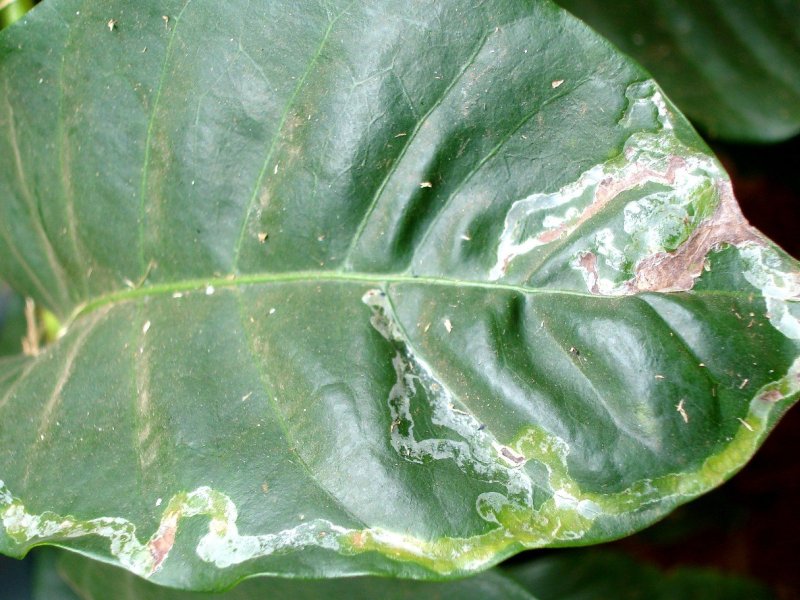
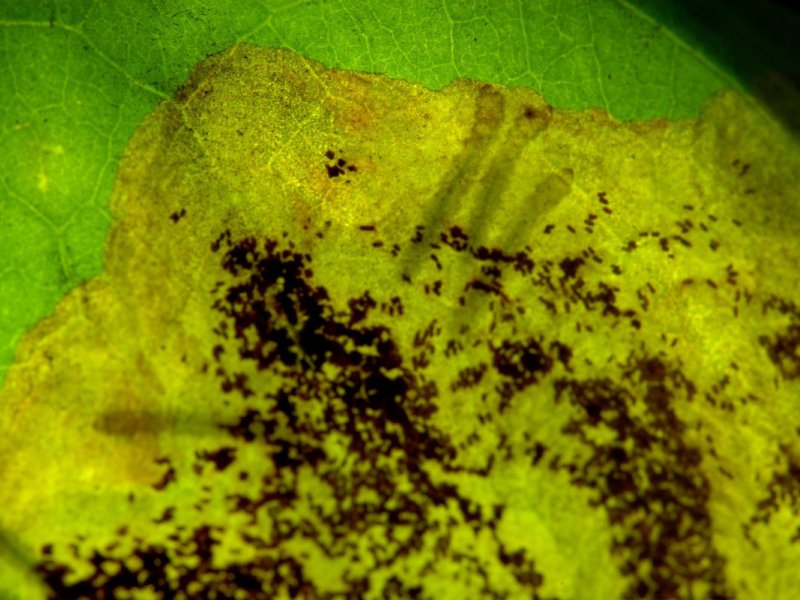
Coffea leaf rust (Hemileia vastatrix) It is the major disease in Arabica coffee. Yellow to orange powdery blotches appear on the underside of leaves, chlorotic patches appear on the upper side. They grow from 2-3 mm diameter to several centimetres. On older leaves, several lesions can merge together. This produces irregular diseased areas covering much of the leaf. However, diseased leaves are usually shed before this stage. A major effect of coffee leaf rust is that it causes defoliation. The disease is spread by spores from lesions on the underside of leaves by wind and rain. Under humid conditions, hyper-parasitic fungi such as Verticillium lecanii grow over the lesions, which produces a pale mycelial growth. Leaf rust is favoured by wet, warm weather. Rainstorms of 7.5 mm or more are needed to cause disease outbreak.
|
|
|
What to do:
|
|
Coffee wilt (Fusarium xylarioides) Indicative symptoms include wilting, chlorosis and defoliation of the aerial parts of the crop, and numerous vertical and spiral cracks in the bark of the trunk. Inspection under the bark, especially around the collar, will reveal characteristic blue-black streaks in the wood. Fungal fruiting bodies (stromata) producing spores can be observed in the bark. Infected berries turn red and appear to ripen early. Seed infection causes blue-black discolouration of the parchment and silver skin. Spores are spread by wind, rain and through human activities (harvesting, pruning etc.). The pathogen can penetrate through wounds so any agency causing wounds will aid the spread of the fungus. Insects may also spread the disease from tree to tree.
Seed from infected berries may contain the pathogen and seed-borne infection is one way in which the disease is spread. Seedborne infection is responsible for seedling blight where the cotyledons fail to unfold, the stem becomes necrotic and the seedling dies. Infected seedlings often survive the nursery stage and later develop collar rot.
The fungus is soil-inhabiting and can penetrate through wounds in the aerial parts or superficial roots. The incubation period from first symptoms to death of the tree varies from days in young plants to 8 months in trees more than 10 years old, although most affected trees die 2-3 months after initial symptoms are observed.
|
|
|
What to do:
|
|
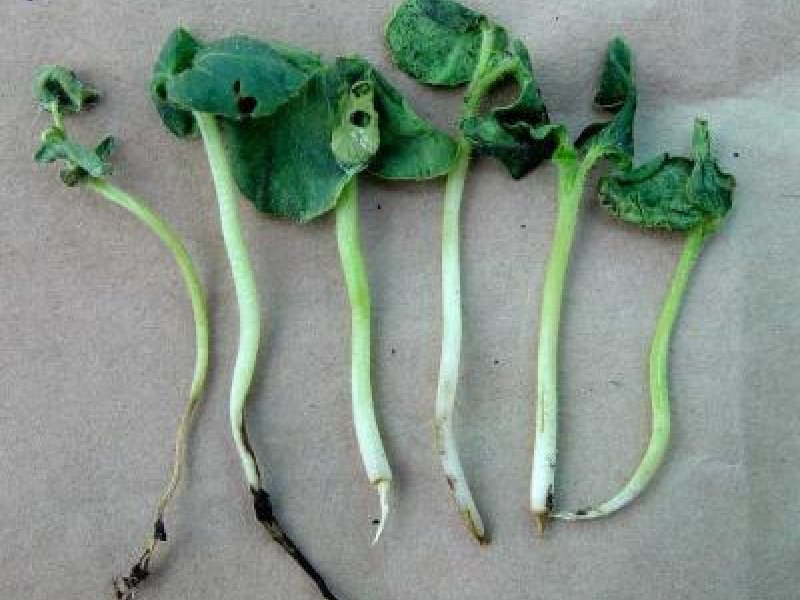
Damping-off diseases (Rhizoctonia solani and Pythium spp.) Damping-off affects coffee-seedlings in nurseries. It is caused by a complex of soil-inhabiting fungi such as Rhizoctonia solani and Pythium spp. It should not be a problem in well-maintained coffee nurseries. Factors that predispose plants to attack include over watering, over shading and acid soil.
|
|
|
What to do:
|
|
Fusarium Bark Disease (Fusarium stilboides) Not widely spread in Kenya except in Taita Taveta District and Makuyu area in Eastern Province. It occurs in 3 different forms and not necessarily all forms present at the same time:
1. Storey's Bark Disease (most common). Suckers attacked at base causing depressed dark brown lesions with yellow margins at times. Pink spore masses are sometimes seen on lesions, which girdle the stem. Girdled old suckers at times continue growing with constriction of bottle neck at base. Weakened suckers may break from wind or picking.
2. Scaly bark (second most common). Bark of the tree rises up in flakes on mature stems. Cankerous regions may develop and die back can follow, though affected stems could also survive.
3. Collar rot. Infection spreads downwards from infected suckers, gradually girdling the tree base. Cankerous lesions develop round stem base at soil level. Constriction appearance may occur and die-back begin from top of tree. Mulching too close to the stem may cause similar rot. Soil- borne fungi may cause seedlings in the nursery to die in the same manner.
|
|
|
What to do:
|
|
Fusarium Root Disease (Fusarium solani) This fungus may stay in the stem and roots for years without symptoms until whole tree suddenly dies. The fungus enters through wounds on roots caused by ploughing, herbicides, die-back, frost or water logging. Symptoms appear when tree is subjected to water stress. If stem is cut near soil level, a purplish pink stain is seen. Dry rot will also show at centre of wood if infection has stayed long. This disease does not spread from tree to tree.
|
|
|
What to do:
|
|
Giant looper (Ascotis selenaria reciprocaria) The adult is a moth with a wingspan of up to 5 cm. They vary in colour from dark brown to light grey with numerous dark grey markings. They lay pale green eggs in crevices in the bark. The caterpillars are pale grey to dark brown resembling twigs, and move with a looping motion. They are about 5 cm when fully grown. Young caterpillars usually eat pits on the upper leaf surface and older caterpillars feed on the leaf margins leaving a jagged edge. All stages of caterpillar prefer tender and young leaves but berries and large flower buds may also be attacked. Alternate hosts include groundnuts, sweet potatoes, black jack weeds as well as some tree species like Datura and Eucalyptus.
|
|
|
What to do:
|
|
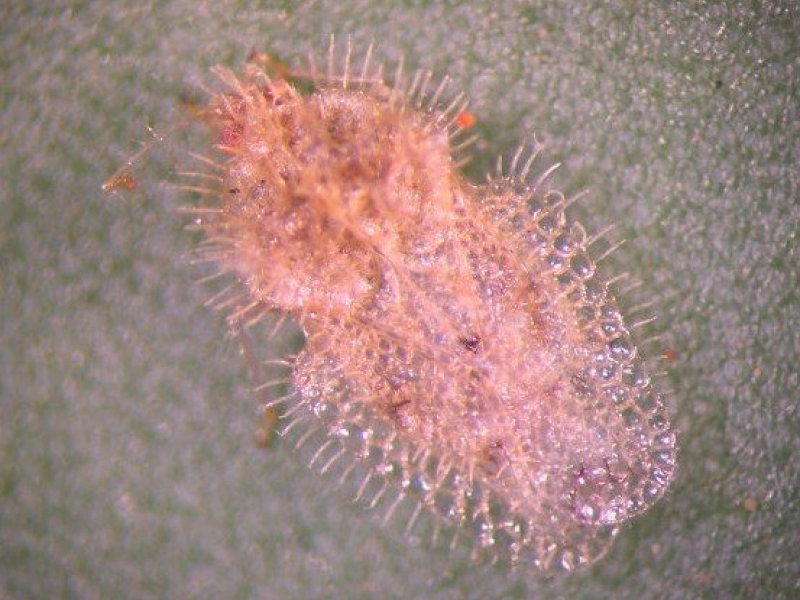
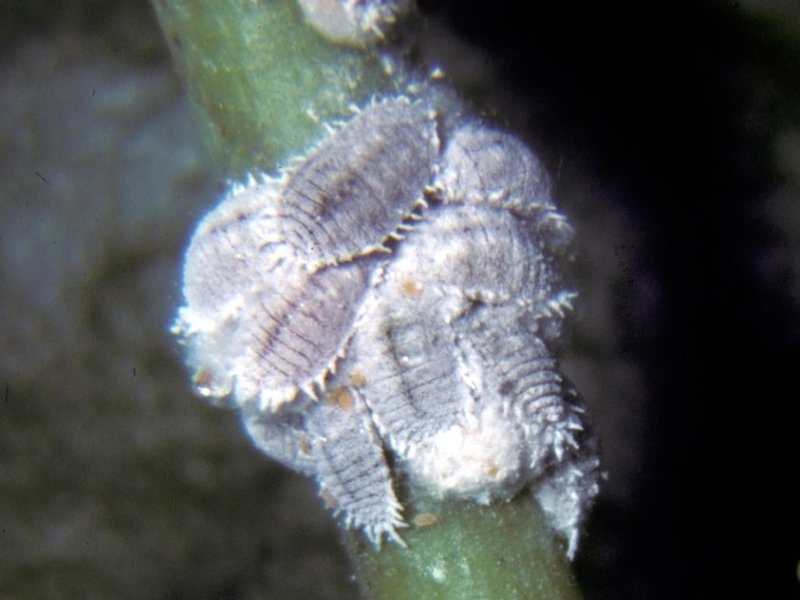
Kenya mealybug (Planococcus kenyae) This mealybug was a major pest of coffee in Kenya in the 20's and 30's in the East Rift area, but it was successfully controlled with introduction of natural enemies from Uganda. Sporadically severe attacks occur especially in the colder months of the year. The mealybugs appear as white masses between clusters of berries and flower buds or sucker tops. They are often attended by ants, which feed on the sticky honeydew excreted by the mealybugs. Honeydew leads to growing of black sooty mould on the upper surfaces of leaves.
|
|
|
What to do:
|
|
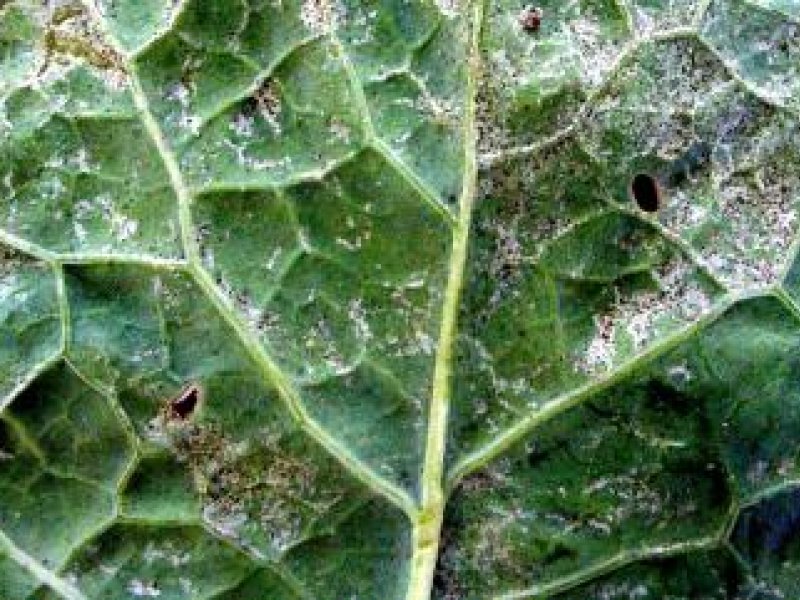
Lace bug (Habrochila placida) This bug is (adult is about 4 mm long) and has wings with a lace-like pattern, hence its common name. The nymphs have knob-like projections on the head of the body. Both adults and nymphs suck on the leaves. Nymphs always feed in groups on the underside of the leaf. Their feeding causes yellow patches on the leaves. The underside of affected leaves is covered with spots of black liquid excreta. In case of severe attack the leaves turn yellow and drop-off. This bug is a sporadically severe pest in Kenya and Tanzania, causing severe defoliation. The attack is often first confined to the lower leaves of a small group of coffee trees. They are most common in hot dry weather. Outbreaks have been associated with injudicious use of pesticides.
|
|
|
What to do:
|
|
Leaf skeletoniser (Leucoplema dohertyi) The leaf skeletoniser is normally a minor pest but severe outbreaks could occur especially in nurseries.
The adult is a grey and brown moth with a wing-span of about 1.3 cm. It is often found on leaves during the day with the hind wings drawn back alongside of the body and the narrow forewings held at right angles to the body. They lay yellow-green eggs (0.5 mm in diameter) singly or in small groups mainly on the underside of leaves. The caterpillars are greyish white with many pimple-like projections on the body. They turn red the day before pupation. Fully-grown caterpillars are about 8 mm long. They feed on underside of the leaf, usually near the near mid-rib leaving many irregular lace-like patches.
|
|
|
What to do:
|
|
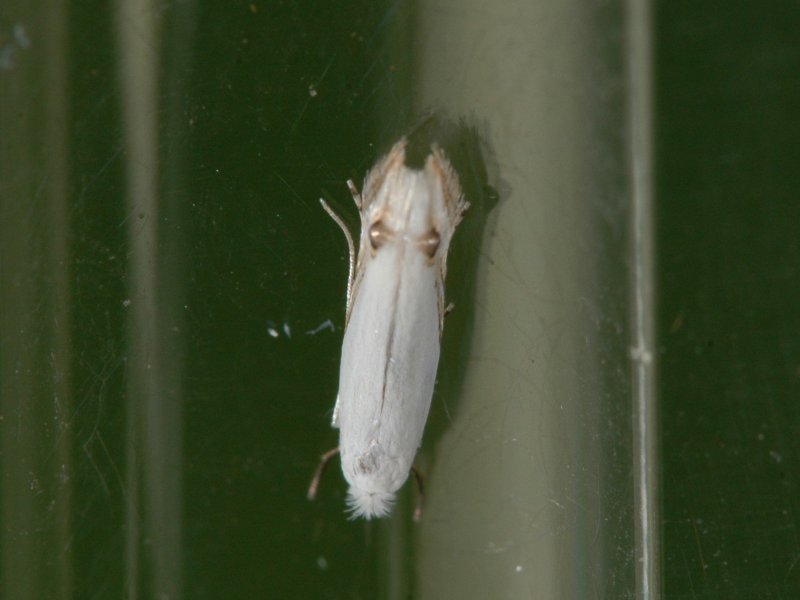
Leafmining caterpillars (Leucoptera meyricki and Leucoptera caffeina) The adults of leafminers are very small (3-4 mm long) white moths. They lay very small eggs (just visible to the naked eye) on the upper leaf surface scattered in small groups (L. meyricki) or touching each other in a neat row along a main vein (L. caffeina). Upon hatching, the caterpillars bore into the leaf and mine just below the upper leaf surface. The mines of each L. meyricki caterpillar are initially separated but after few days they join to form one large mine. The young caterpillars of L. caffeine produce one communal mine. These mines appear as irregular brown blotches on upper side of leaves, which when opened reveals many whitish caterpillars. Caterpillars are flattened, white and very small (4-8 mm when fully grown). Mature caterpillars come out of the mine and pupate in a H- shaped cocoon (6 mm long) on dead leaves on the ground or on the underside of leaves on the tree. The mining activity causes a reduction of the active leaf surface, reducing assimilation. Attacked leaves are usually shed prematurely. Leafminers can live on shrubs belonging to the same family as coffee (Rubiaceae family).
|
|
|
What to do:
|
|
Root mealybug (Planococcus citri) This mealybug is usually a minor pest of coffee, but it is potentially a serious pest. The mealybugs attack the roots where they usually live in association with a fungus (Polyporus sp.), which forms a crust over the mealybugs. Seedlings and very young trees are often free of the fungus. Attacked trees show wilting yellow leaves as if suffering from moisture stress. When affected trees are uprooted, the roots are stunted and encased in brown fungus. When the fungus is pealed off, the white mealybugs can be seen.
Damage is more prominent in dry conditions. The pest is associated with poorly established coffee. Severe infestation may lead to loss of quality, failure of berries to ripen and overbearing and die-back. Identical mealybugs have been reported on Solanum spp., Combretum spp. and Indigofera spp. The root mealybug is also known as the citrus mealybug. It also attacks citrus and cocoa, where it normally attacks the aerial part of the plants.
In the highlands of Java, the shade tree Leucaena glauca is main food plant of citrus mealybug at altitudes above 600m (2000 ft.). Measures that proved successful for the control of citrus mealybug were mainly directed against infestation of this tree and consisted of removing the flower clusters or, when necessary, pruning all foliage and flowers. It is also claimed that citrus mealybug can be controlled by increasing the shade in plantations and that this was undesirable for Robusta coffee but suitable for Arabica at high altitudes. Good results were obtained by providing three covers, one above the other, of Leucaena, Erythrina and Albizia, or with Leucaena and Albizia only. It is further suggested that because the insect infests mainly the flowers and pods of L. glauca, other shade trees that seldom flower, such as L. pulverulenta (L. leucocephala), or a sterile hybrid of L. glauca and L. glabrosa should be planted. |
|
|
What to do:
|
|
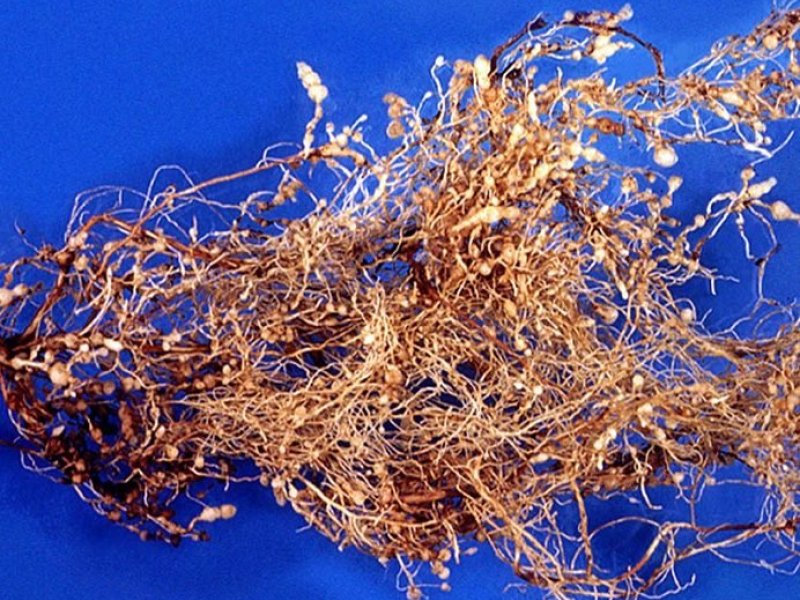
Root-knot nematodes (Meloidogyne spp.) Important nematodes attacking both Arabica and Robusta coffee are Meloidogyne arenaria, Meloidogyne decalineata and Meloidogyne incognita, causing root knots and galls. Other nematode species include Pratylenchus coffeae, Radopholus similis, Rotylenchus iperoiguensis and Rotylenchus pararobustus.
Field symptoms are typically of stunted, poorly growing plants with yellowing leaves. Infected root systems show characteristic knots or galls, the severity of which varies with the degree of nematode infection and species and variety of plant parasitized. Strategies of cultural control are less well developed and crop rotations are difficult to design because of the wide host range of Root-knot nematodes. Groundnuts or maize, which are both poor or non-hosts to M. incognita, have been evaluated for use in cropping systems designed to manage this nematode. |
|
|
What to do:
|
|
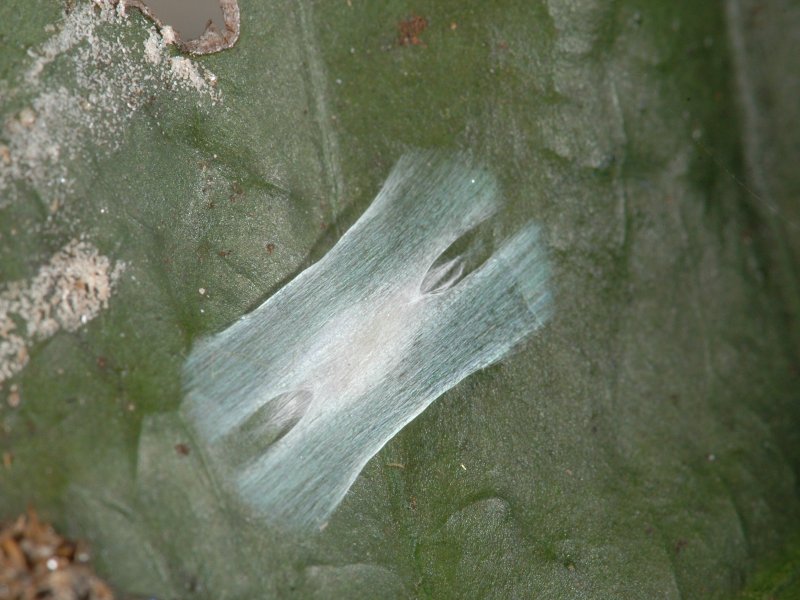
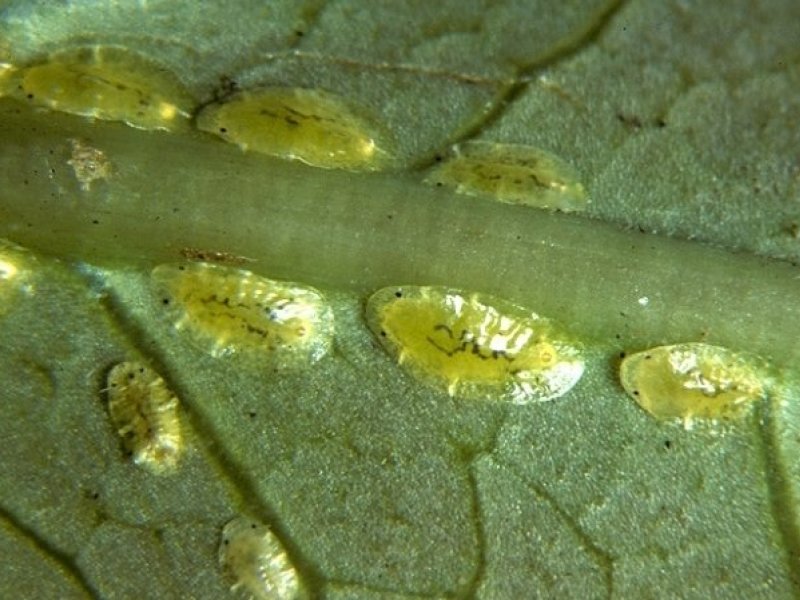
Soft green scale (Coccus alpinus/ C. viridis) Various species of scales attack coffee in East Africa. The soft green scales are common but minor pests of Arabica coffee. More serious on transplanted seedlings during the first 2 years in the field. The yellowish to greenish flat oval scales are about 5 mm in length. They prefer to attack green wood and leaves, and usually appear as rows of flat oval green scales along main leaf vein and near tips of green shoots. Soft green scales produce large amounts of honeydew. This honeydew attracts ants, which while tending the scales protect them from their natural enemies. The sticky honeydew covers the leaves and sooty mould develops on it. As a result leaves appear black and sticky. Too dry microclimate favours infestation with soft green scale.
|
|
|
What to do:
|
|
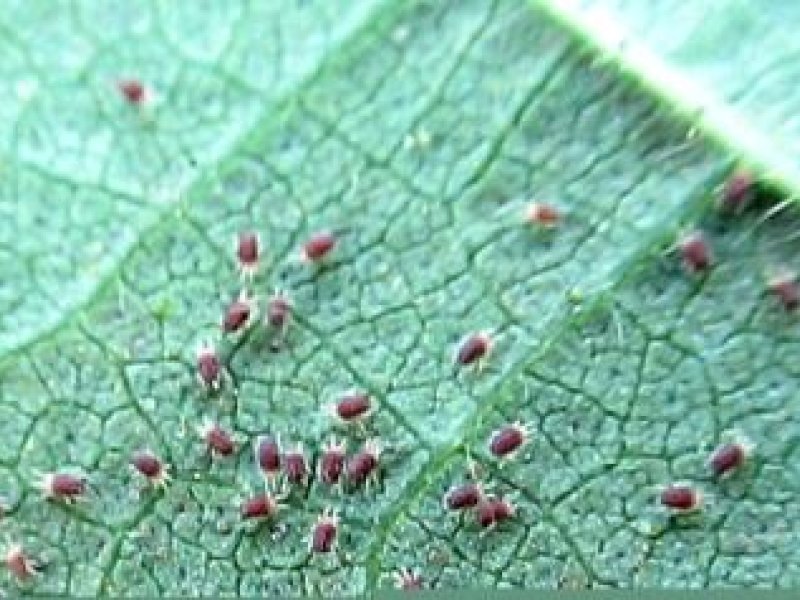
Red coffee mite (Oligonychus coffeae) The red coffee mite may be a pest of unshaded coffee in localised attacks during the dry season. They attack the upper surface of mature leaves. As a result the upper surface of fully hardened leaves turn a rusty, purple or yellow brown colour. Under drought stress young leaves may also be attacked.
|
|
|
What to do:
|
|
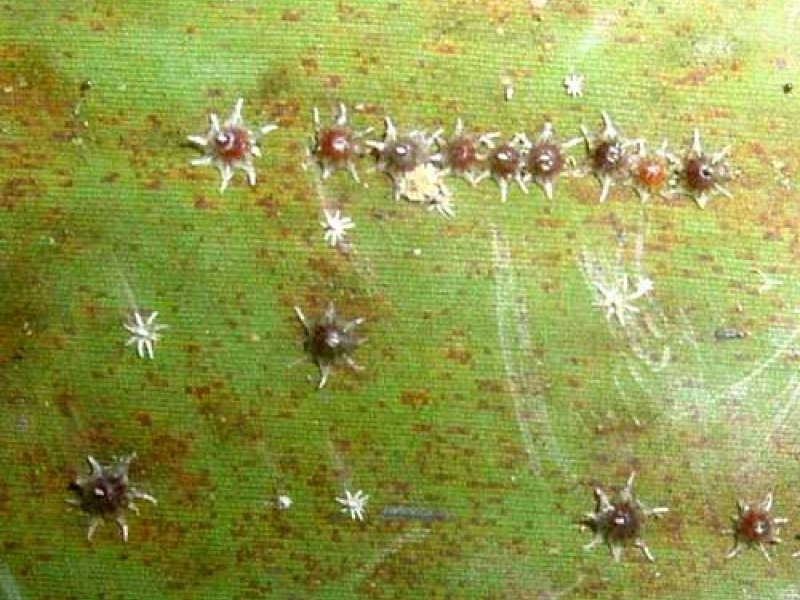
Star scale (Asterolecanium coffeae) It is yellowish to reddish brown, covered with numerous small spines. It attacks stems and branches, causing deformation of branches. The growth of trees severely attacked is retarded and the trees may be die. Symptoms include green branches bent at nodes with pits in green bark beneath the bend, drooping dead leaves on affected nodes and numerous small red or yellow objects are found in the bark crevices especially near the ground. Alternative hosts include Jacaranda and loquat trees.
|
|
|
What to do:
|
|
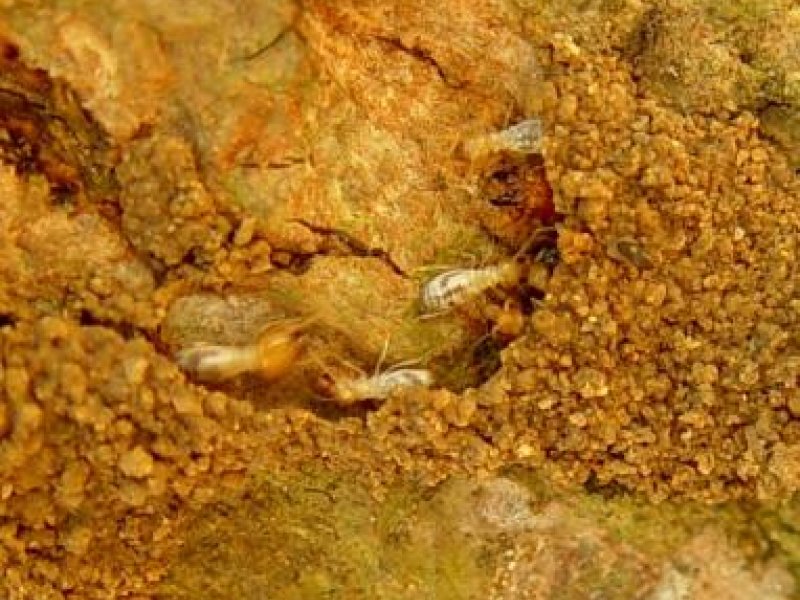
Termites Termites can be a serious problem for coconut palms, particularly for young trees in tree nurseries or trees that have just been transplanted into the field. Termites live in the soil in hills, construct tunnel from the hills to the palms and feed on all parts of young coconut palms. Damage occurs mainly during the dry season.
Many plants have a repellent or even insecticidal effect on termites and can be applied as spray directly against termites or as barrier around the trunk of coconut palms:
|
|
|
What to do:
|
|
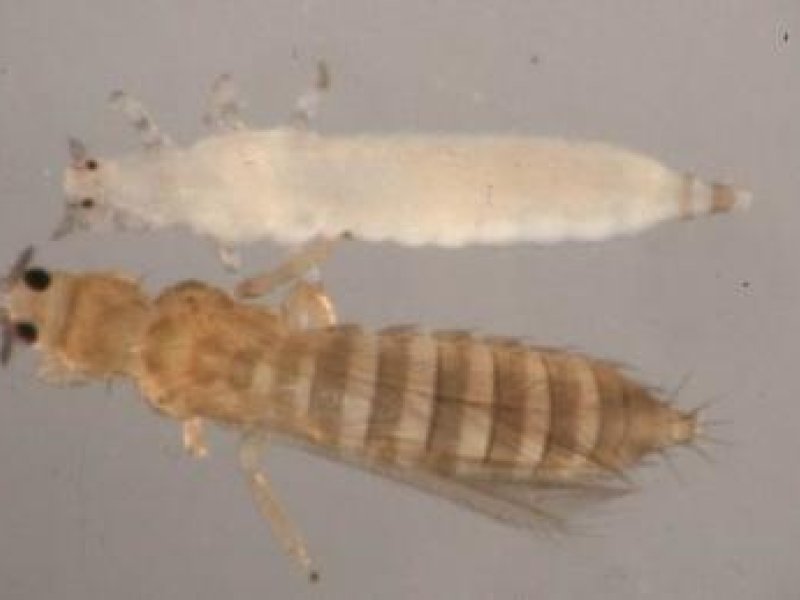
Coffee thrips (Diarthrothrips coffeae) The adult thrips are 1-1.5 mm in length and grey-brown in colour. The nymphs are wingless and yellow. Both adults and nymphs feed on the underside of leaves, but in severe infestations they also attack the upper side of leaves, berries and green shoots. Attacked plant parts show irregular grey or silvery patches covered by numerous tiny black spots, which are the excreta of the thrips. In case of severe infestation the leaves dry up and fall off. Heavy outbreaks occur during periods of drought and high temperatures.
|
|
|
What to do:
|
|
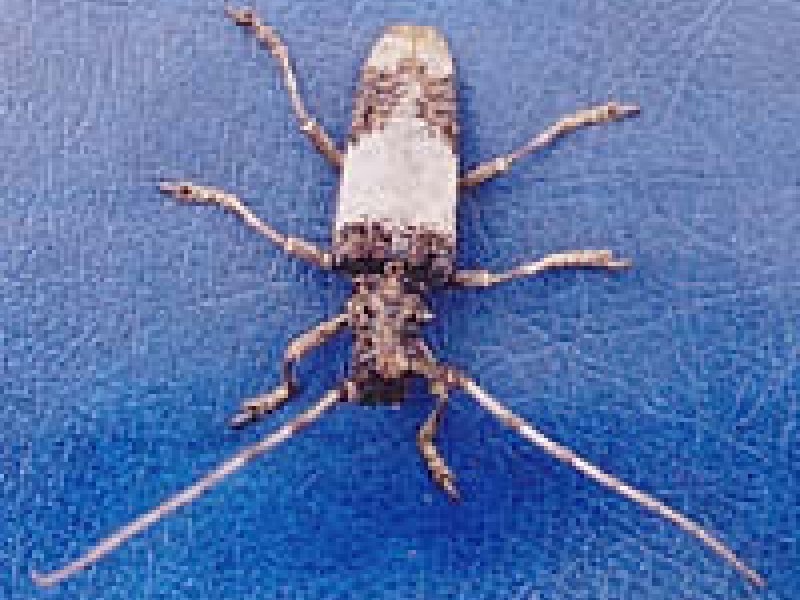
White coffee borer (Anthores leuconotus) Adult beetles of the white coffee borer (also called white stemborer) are about 3 cm long and have very long antenna. They are dark brown greyish in colour; the wing cases are greyish white with dark markings near the end. Adult beetles feed on the bark of branches, causing little damage. Female beetles lay eggs on the trunks of trees usually at the base near the ground level. The whitish, legless larva burrows into the bark and the wood of the trunk and main roots. The larva pupates in a large chamber within the trunk. The attack by larvae causes serious damage, particularly if the trunks are almost ring-barked. Young trees may be killed.
Older trees wilt, turn yellow and produce a poor crop. Symptoms of attack are round exit holes of the adult beetles in the trunk and wood shaving extruding from the bark or from the roots just below soil level. The white borer can become a serious pest especially below 1500 m (5000 ft) on shallow or eroded soil near shade trees.
|
|
|
What to do:
|
Geographical Distribution in Africa
Geographical Distribution of Coffee in Africa. updated on 8th July 2019 source FAOSTAT
General Information and Agronomic Aspects
Coffee is one of the most important cash crops in Kenya. It is grown in large-scale plantations (42,000 ha from 2001-2005) as well as by small-scale holders (128,000 ha) giving a total production of about 50,000 tons annually. The main variety in Kenya is Arabica coffee (C. arabica).
The stimulating effect of the coffee beverage is largely derived from the alkaloid caffeine, but cured beans have to be roasted and finely ground to bring out the characteristic coffee aroma. In some producer countries, roasting of locally available coffee in the home is very common and the brew is prepared by pouring hot water over freshly roasted and ground coffee beans.
An important constituent of the coffee bean is caffeine. The free caffeine content in a bean is dependant on the coffee type, variety, the site conditions and other factors, and can be more than 2.5%.
Economically, the most important coffee varieties are Coffea arabica called "Arabica" and Coffea canephora called "Robusta". The latter yields about 30% more than "Arabica", albeit its price is around 30% lower.
Coffee is mainly grown as a beverage, though the plant residues can provide fuel (coffee charcoal or wood) and a good mulch.
Until now, organic cultivation has been of less importance in such countries as Ethiopia, Kenya and Mozambique. It is mostly organic "Arabica" that is being cultivated. "Robusta" is currently barely available in certified organic quality.
Nutritive value per 100 g of edible portion
| Raw or Cooked Coffee | Food Energy (Calories / %Daily Value*) |
Carbohydrates (g / %DV) |
Fat (g / %DV) |
Protein (g / %DV) |
Calcium (g / %DV) |
Phosphorus (mg / %DV) |
Iron (mg / %DV) |
Potassium (mg / %DV) |
Vitamin A (I.U) |
Vitamin C (I.U) |
Vitamin B 6 (I.U) |
Vitamin B 12 (I.U) |
Thiamine (mg / %DV) |
Riboflavin (mg / %DV) |
Ash (g / %DV) |
| Coffee brewed from grounded berries | 1.0 / 0% | 0.0 / 0% | 0.0 / 0% | 0.1 / 0% | 2.0 / 0% | 3.0 / 0% | 0.0 / 0% | 49.0 / 1% | 0.0 IU / 0% | 0.0 / 0% | 0.0 / 0% | 0.0 / 0% | 0.0 / 1% | 0.1 / 4% | 0.4 |
*Percent Daily Values (DV) are based on a 2000 calorie diet. Your daily values may be higher or lower, depending on your calorie needs.
Climate conditions, soil and water management
The ideal temperature range for Arabica coffee lies between 18 and 24º C. Maximum day temperatures should not exceed 30ºC and night temperatures should not fall below 15°C. At higher temperatures, bud formation and growth are stimulated. Low temperature or wide daily temperature variation may result in distortion, yellowing and cracking of the leaves and tip growth, a condition known as "Hot and Cold" or crinkle heat. Arabica coffee is normally grown at altitudes from 1400 to 2000 m (4,500-6,800 ft) with a rainfall of not less than 1000 mm per year. Where coffee is grown under conditions of minimum rainfall, mulching is essential to conserve moisture.
Robusta coffee is more resistant to pest infestation and is well adapted to warm and humid equatorial climates with average temperatures of 22-26°C, minimum not below 10°C at altitudes of 100-800 m, and well-distributed annual rainfall of 2000 mm or more. The ideal amount of rainfall lies between 1500 and 1900 mm. Coffee reacts positively to a drought period, which should nevertheless not be longer than 3 months. The rainfall should be evenly spread throughout the rest of the year. Irregular rainfall causes uneven blossoms and fruit maturity. Coffee is a half-shade plant, which can only utilise around 1% of the sunlight for photosynthesis. At leaf temperatures over 34º C, assimilation is practically zero, meaning that the rate of photosynthesis of a shaded plant is actually higher than that of a plant fully exposed to the sun.
As a rule: Grow in lower regions Robusta and in higher regions Arabica. The borderline is variable, and lies around 1400 m in Kenya. The berry borer and coffee rust are important indicators as to whether the coffee variety is suited to the site conditions. For example, an Arabica plantation at 1200 m, which is heavily infeced with coffee rust and infected by berry borer, despite sufficient shade, is an indication that the variety is ill-suited to the site, and should, in time, be replaced with Robusta.
Coffee prefers well-drained and airy soils. It needs free drainage to a depth of at least 1.5 m and 3 m in drier areas. Humus-rich, lightly acidic soils (pH range 4.4-5.4) are beneficial; the best conditions are those to be found on virgin soils of volcanic origin. The topsoil should contain at least 2% humus.
Propagation and planting
| Variety | Altitude | Spacing Density | Attributes |
| 'Ruiru II' | All coffee growing areas | 2 x 2 m (6 x 6 ft) 2500 trees/ha |
|
| 'SL 34' | High altitude with good rainfall | 2.75 x 2.75 m (9 x 9 ft) 1330 trees/ha |
|
| 'Sl 28' | Medium to high altitude coffee zones without serious leaf rust | 2.75 x 2.75 m (9 x 9 ft) 1330 trees/ha |
|
| 'K7' | Low altitude | 2.75 x 2.75 m (9 x 9 ft) |
|
Vegetative propagation can be done by rooting of cuttings, grafting, top-working and micro propagation (tissue culture). Major considerations for vegetative propagation are:
Choice of mother trees.
- These trees are derived from seedlings that have undergone a pre-selection test for coffee berry disease and coffee leaf rust resistance.
- Establishment of a clonal garden. The selected mother trees are established in the field as per the recommended spacing of 1m x 1m. After 12-18 months, the primary branches are removed and the stems bent and pegged down in a horizontal position to encourage growth of orthotropic (vertical) shoots.
Construction of a propagator:
- The propagators whose width measures 0.75 m (2.5 ft) are constructed on a 60 cm foundation with a wall that rises another 50 cm above the ground.
- To achieve good drainage, the first 15 cm from the ground level are filled with gravel covered by a layer of sand of about 7.5 cm. Finally a 15 cm rooting medium is placed on top of the sand. Recommended rooting media is either of the following: a) sawdust from cypress trees, b) pure river sand or c) sub-soil, all free from any contamination.
- The propagator should be provided with a watering system (mini sprinklers) with emitters at 150 cm spacing.
- To regulate relative humidity, the propagators are covered with clear polythene sheeting, gauge 1000 suspended 1 m above the rooting medium on steel or wooden frames. Shade is normally erected about 2.75 m (9ft) from the ground. The recommended materials for shade are sisal/bamboo poles, shade net (75% shade) or interwoven nets.
Propagation of rooted cuttings:
- Suckers are harvested from the mother trees when they are 6 months old and bearing 6 internodes. Harvesting is done early in the morning when the atmospheric relative humidity is high.
- Single node cuttings are prepared by making a cut at an angle below the node but retaining the pair of leaves.
- The cuttings are planted in propagators at a depth of 2-4 cm and a spacing of 4 cm x 4 cm. Callus formation begins 3 weeks after planting and is complete in 5-6 weeks. (callus formation is the healing of the cut edge of the cutting in the rooting media).
- Root development follows after 8-10 weeks
- The rooted cuttings are transplanted at 12-14 weeks into black polybags measuring 12.5 x 22.5 cm (5x9 in), 200 gauge filled with rich composite soil mixture consisting of top soil, river sand and well rotted manure at a ratio of 3:2:1 respectively, all free from any contamination. For organic propagation rock phosphate is added and if insects normally pose a problem, incorporate chopped leaves of Lantana camara or Mexican marigold.
- The potted seedlings are returned to the propagators for a period of 1-2 months to develop more foliage and feeder roots under the same environmental conditions.
The planting materials are then taken care of as per the nursery recommendations.
- Grafting: This is the successful healing of the union between the scion and the rootstock. Grafting requires 10-12 month old seedlings (or pencil thick) to be used as rootstock. Rootstocks of the commercially existing Arabica varieties are compatible with 'Ruiru II'. The graft union is tied with a polythene tape and the entire seedling is placed in a propagator to heal.
- Topworking: This is a cheaper method of converting mature old trees of traditional Arabica coffee into 'Ruiru II' without uprooting and replanting. Sucker growth is induced on the trees to be converted by side pruning. Six month old healthy suckers are selected and grafted with single node scions of 'Ruiru II' bearing a pair of leaves. The graft union is tied with polythene tape to keep the scion in place. Advantages of Topworking:
- A farm can be converted from the traditional cultivars ('SL 28', 'SL 34' or 'K7') to 'Ruiru II' without interfering with normal cropping pattern.
- The farmer saves on cost of uprooting old bushes and new establishment costs.
- The well-established root system of old stumps prevents lodging, which may occur when young "Ruiru II" trees carry a heavy crop.
Coffee Nursery Management
Most cultivars of the self-pollinating Arabica coffee are practically pure lines, propagated by seed. In Kenya, F1 hybrid seeds are produced by hand-pollination of new disease-resistant Arabica cultivars, and certified seed can be obtained from the Coffee Research Foundation in Ruiru.
- The nursery site should be selected on level to gently sloping ground. On sloping ground of 4-5 % it should be bench terraced, sheltered from strong winds, near a permanent reliable water source, accessible and free from weeds.
- The bed construction should be 1m (3 ft) wide with a shade 60 cm (2 ft) above the bed.
- Plant only certified disease free seed from the Coffee Research Foundation (CRF). Sow immediately after collection to avoid loss of viability in order to ensure high germination rate. Remove the husks to reduce germination period. 1 kg seed contains an average of 3,000 seeds.
- Germinate in river sand beds of 5-7 cm (2-3 in) depth with a spacing of 2.5 x 2.5 cm (1 in) and 1 cm (1/2 in) deep. Apply a thin mulch cover. Shade 60 cm above the bed. Water adequately (avoid waterlogging)
- .Remove mulch when seeds have germinated.
- Seedlings emerge after 4 weeks and take another 4 weeks before they are transplanted to polybags
- Transplant pre-germs at the leaf stage into polybags. Avoid deep planting. This ensures minimal disturbance to roots during transplanting, and makes long distance transportation more convenient. Also field establishment can wait till the weather is favourable.
- Renew seed bed and river sand every time new seeds are being planted
- Potting mixture: top soil: 3, sand: 2, well rotted manure or compost: 1. To this mixture add phosphorous, for organic farming a handful of rock phosphate to about 6 "debes" (debe = 20 litre bucket) of mixture as well as neem cake or chopped up leaves of Mexican marigold or Lantana camara for insect control.
- Water seedlings at 2 times a week and control weeds by hand weeding. Control diseases (damping off, leaf rust and Brown eye spot ) using 0.5 % Copper solution, and control insect pests when noticed.
- Shading. Put a shed at 120 cm (4 ft) above the polybed, and provide dense shade initially. Harden the seedlings by gradually reducing the shade. Reduce the shade by half when the seedlings are 8-9 months old and completely 1 month beforetransplanting.farmyard manure or well rotted coffee pulp plus 200 g rock phosphate. If the soil is acidic add 100 g dolomitic limestone (CaCO3 MgCO3).
Land preparation
Land cleared of trees within 6 months should not be used for coffee because of the risk of Armillaria , a fungal disease which causes root rot.
Clear land well in advance, digging out all stumps, bushes and grasses such as kikuyu grass and couch grass. If the land has steep slopes, make terraces or other conservation structures. Protect bench terraces by planting grasses e.g. Paspulum notatum on the bench faces. Planting holes should be dug 3 months before the onset of rains to allow weathering.
Fill the holes 4 weeks before planting with a top soil mixed with 1 "debe" (20 litre bucket) farmyard manure or well rotted coffee pulp plus 200 g rock phosphate. If the soil is acidic add 100 g dolomitic limestone (CaCO3 MgCO3).
Planting
Dig holes of size 60 cm x 60 cm x 60 cm at a spacing of 2.75m x 2.75m for the traditional varieties ("SL28", "SL34" and "K7"). A closer spacing of 2m x 1 m on flat land for small holders without spray roads is recommended. Spacing for "Ruiru II" is 2 x 2 m or 2 x 1 m giving a population density of 2,500 - 3,300 trees/ha for small holders. Transplant potted seedlings when they are about 30-40 cm high with maturing bark about 15 cm (6 in) and 2-3 pairs of lateral branches at about 12-15 months old.
Mulching
Mulching has several benefits to coffee e.g. conservation of moisture during dry spells, suppression of weed growth, nutrient supply, improvement of soil structure and water infiltration, checking of soil erosion and top soil temperature as well as reduction of thrips incidence. Mulching also enhances root development in the fertile top soil and thus a general yield increase. Examples of mulching material include napier grass (half an acre of napier grass gives enough mulch for 1 ha (2.5 acres) of coffee land), sisal waste, coffee prunings, maize and banana trash. When using coffee prunings, take care that no pests (leafminers, mealybugs, etc.) are on the prunings otherwise they could re-infest the trees.
Shade trees and windbreaks
Plant shade trees 1 year before coffee transplanting is required. Common shade trees are leucaena (Leucaena leucocephala) and mother of cocoa (Gliricidia sepium). Also Grevillea robusta, Albizia spp and Cordia abyssinica are recommended shade trees. (See also below under Diversification Strategies). With intensive cultivation and optimum inputs, higher yields are obtained with unshaded coffee, but shade will prevent overbearing and shoot dieback under lower standards of crop management or suboptimal ecological conditions.
Husbandry
Coffee grows best with shade trees. Shade trees reduce stress in coffee. Avoid extracting timber at random for short-term gains. Maintain a two-layer canopy consisting of temporary and permanent shade trees like coconut, Ficus species, Albizzia species, jack fruit, and citrus, etc. At higher altitudes temporary shade trees may be phased out once the coffee is well-established. Regulate shade every year instead of once in 3-4 years to minimize damage to coffee bushes. Shade tree selection and management are important because better shade may decrease the incidence of some important pests and diseases. Suppressing of weeds, particularly East African couch grass (Digitaria scalarum) and Kikuyu grass, by careful tillage (not damaging the superficial feeder roots of the coffee), mulching and/or leguminous cover crops, is very important.
Fertiliser requirements depend on crop level and nutrient status of the soil. Nutrients removed by harvesting 6 t of fruits of Robusta coffee, equivalent to 1 t of green beans, are: 35 kg N, 6 kg P2O5, 50 kg K2O, 4 kg CaO, 4 kg MgO, 0.3 kg Fe2O3 and 0.02 kg Mn3O4. Return coffee pulps and hulls as organic fertilizer in coffee fields. These are rich in nutrients. A 60 kg bag of coffee pulps/hulls contains: 1 kg N; 0.60 kg P; .09 kg K and other trace elements.
Mulching using dried banana leaves and cut dried grass conserves soil moisture, protects soil from compaction, and reduces soil acidity.
Pruning
Pruning is essential in coffee production:
(a) to determine the shape of the tree
(b) to maximise the amount of new wood for the next season's crop (c) to maintain a correct balance between leaf area and crop and
(d) to prevent over-bearing and thus reduce biennial production or death of trees.
Unpruned coffee usually produces a heavy crop one year and a lighter crop the next season. Pruning makes trees more manageable and easier to pick and spray. Diseases and insect pests can also do more damage in unpruned coffee, as they tend to build up in the older branches.

A well pruned, young coffee plant (Coffea arabica) .
Advantages include:
- Suitable crop : leaf ratio
- Uniform yearly cropping
- Good light and air penetration and circulation for better fruiting and bringing vigour to the tree
When to prune:
Immediately after main crop harvesting. Sick-looking trees due to die back to be pruned only after new growth. Trees attacked by star scales to be pruned after the main crop to avoid carrying the scales to other trees.
Multiple stem pruning: The tree normally has 3 stems and the crop is borne on laterals. Each.lateral bears 2 crops and is then pruned. The crop is therefore borne higher up the tree each year. Every 4-6 years a new cycle is started. This is done by selecting 3 new suckers, which will replace the original stems. In multiple stem pruning, 4 basic operations are carried out:
1. Main pruning: Regulating the number and spacing of primary branches.
2. Secondary pruning: Also known as "handling", involves regulating number and spacing of secondary branches.
3. Sucker control: Removal of unwanted growing shoots called "suckers" (remove them with the meristem, otherwise you multiply suckers)
4. Change of cycle: Selection of some "suckers" to grow into new bearing stems.
How to prune:
Please discuss with a CRF (Coffee Research Foundation) field officer or read CRF Technical Circular No 301: Canopy Management in Coffee, as the recommendations differ from different ecological zones.
Diversification strategies
1 ) Crops of the upperstorey (shade)
They create large amounts of organic material and humus and at the same time protect the coffee tree against too much sun. The alternation in yield can be reduced, and the life-time of the plantation is increased. Shade also has an immense influence on the quality of the coffee, but it also reduces the yield (fewer coffee trees per area unit). Shading trees also reduce weeds: When an optimum density of coffee and shading trees is reached, tilling weeds is hardly necessary anymore. Shading trees protects against soil erosion and improves the micro-climate on the plantation. By choosing the correct varieties and cultivation method for the shading trees, the micro-climate can be influenced at any point in time. This is very important to regulate pests. Fruit trees offer a diversification for the farmer's diet and economic base. Precious woods can provide a long-term increase in value of the site: along with other varieties, they can provide wood for construction and fuel. Shading trees also creates more pleasant working temperatures on the plantation.
No figures can be offered for the optimum shade density, as this depends on the local site conditions and the state of the plantation. A rule of thumb says that the shade should be around 50%. The higher in altitude the coffee plot lies, the less the distances should be between the coffee bushes and start of the shading roof. At the upper growth limits for coffee plants, the shading plants are therefore at around the same height as them. Care should be taken to trim the shading plants synchronously to the coffee blossoming (6-8 weeks before the blossom). Blossom formation can thereby be assisted and synchronised.
2 ) Crops of the middle storey
As with the shading plants, the variation of varieties used for the middle crop should be adapted to the local site conditions. They can be chosen according to the need for fruits and additional products for each individual plantation. Bananas should, if possible, always be integrated as an additional crop. They are well suited to providing temporary shade, and for 'drying out' of the wetter parts of a plantation. Their ability to mobilise potassium reserves in the soil, and to make them available for the coffee treess is very important. A whole diversity of combinations with other fruit trees can be integrated into the system: citrus planted together with avocado, are especially good for sites that enjoy intensive sunlight.
3 ) Crops of the under storey
On sites which are not optimal (e.g. too dry or poor in nutrients), it makes sense to replace the natural vegetation in the under storey with green manuring plants (legumes). The bottom crops should never be allowed to dominate and completely displace the natural vegetation. Many varieties are suitable as bottom crops. They should be selected according to the amount of shade they provide, soil conditions and rainfall. In principle, bottom crops should be sown on new plantations, or when the shading trees and coffee bushes are being trimmed. Otherwise there will not be enough light on an organic coffee plantation for the bottom crops. It is very important to sow perennial, non-climbing and not very aggressively growing legumes. Otherwise there is a danger of the coffee plantation becoming overgrown e.g. with tropical kudzu (Pueraria phaseoloides).
Harvesting
Each year coffee is harvested during the dry season when the coffee cherries are bright red, glossy, and firm. To maximise the amount of ripe coffee harvested it is necessary to selectively pick the ripe beans from the tree by hand and leave behind unripe, green beans to be harvested at a later time. Selective picking of coffee berries at 10-14-day intervals is common where harvesting extends over a period of 7-9 months. Where the harvesting season is shorter, whole branches are stripped when the majority of berries are ripe. Costs of harvesting will be 2-3 times higher for selective picking than strip picking. Deliver berries for processing the same day they are picked.
Pulping must be done on the day coffee is picked as coffee left in the sun will start to ferment. Pulping is done to remove exocarp and mesocarp through the wet processing method after which coffee parchment is obtained. The parchment is then dried in shallow layers on raised tables or trays to moisture content of 10-11%. For more information on processing, please contact Coffee Research Foundation (CRF), Ruiru.
Quality problem
Stinkers are a severe form of over fermented beans. These defective beans will give a bad (unclean, over fermented, pulpy, sour, foul) taste to brewed coffee and will down grade the delivered coffee, causing loss of considerable earnings. Long fermentation times (more than 4 days) and hot temperatures are the main culprits producing these unpleasant beans.
Storage
Coffee stores should be dry, clean and well ventilated. Never store or keep chemicals in a coffee store. Keep fully dry coffee beans on wooden tables or floors or even in ventilated bins. They should be stirred or turned every day for 10 days before bagging. They must be put in sacks as they come from the drying tables. Place bags on wooden battens 15 cm above the ground or concrete floor and away from walls. Do not store close to corrugated iron sheets. Store for a minimum of 4 weeks and a maximum of 6 months. After that beans become woody. A relative humidity in the store of 60% at 20°C is suitable.
| Coffee berry borer (Hypothenemus hampei) It is the most serious pest of coffee in many of the major coffee-producing countries. Crop losses caused by this pest can be severe, ranging from 50 to 100% of berries attacked if the pest is not controlled. The adult is a tiny (about 1.5 to 2.5 mm long), cylindrical blackish beetle. The females (1.4 to 1.6 mm) penetrate into mature green or red berries, usually from the tip and lay eggs within the beans. Female beetles fly from tree to tree to lay eggs. Once the eggs hatch, the larvae feed on the beans, rendering them unsuitable for commerce or greatly lowering their quality. The white, legless grubs have a brown head. They feed by tunnelling in the tissues of the beans destroying them. Pupation takes place in the berry. Symptoms of attack are one or more small round holes near the apex of large green or ripe berries. The damaged beans, which have a distinct blue-green staining contain up to 20 grubs. Female beetles also attack young berries. Coffee berry borer damage predisposes the coffee bean to fungal infection and hence contamination with mycotoxins (food poison). Reasons for the infestation with coffee berry borer can be: the plantation is at a too low altitude, too much shade or that there are abandoned or infested plantations nearby. Infestations are carried over between peaks of fruiting by breeding in over-ripe berries left on the tree or fallen to the ground.
What to do:
|
| Soft green scale (Coccus alpinus/ C. viridis) Various species of scales attack coffee in East Africa. The soft green scales are common but minor pests of Arabica coffee. More serious on transplanted seedlings during the first 2 years in the field. The yellowish to greenish flat oval scales are about 5 mm in length. They prefer to attack green wood and leaves, and usually appear as rows of flat oval green scales along main leaf vein and near tips of green shoots. Soft green scales produce large amounts of honeydew. This honeydew attracts ants, which while tending the scales protect them from their natural enemies. The sticky honeydew covers the leaves and sooty mould develops on it. As a result leaves appear black and sticky. Too dry microclimate favours infestation with soft green scale.
What to do:
|
| Coffee thrips (Diarthrothrips coffeae) The adult thrips are 1-1.5 mm in length and grey-brown in colour. The nymphs are wingless and yellow. Both adults and nymphs feed on the underside of leaves, but in severe infestations they also attack the upper side of leaves, berries and green shoots. Attacked plant parts show irregular grey or silvery patches covered by numerous tiny black spots, which are the excreta of the thrips. In case of severe infestation the leaves dry up and fall off. Heavy outbreaks occur during periods of drought and high temperatures.
What to do:
|
| This bug is (adult is about 4 mm long) and has wings with a lace-like pattern, hence its common name. The nymphs have knob-like projections on the head of the body. Both adults and nymphs suck on the leaves. Nymphs always feed in groups on the underside of the leaf. Their feeding causes yellow patches on the leaves. The underside of affected leaves is covered with spots of black liquid excreta. In case of severe attack the leaves turn yellow and drop-off. This bug is a sporadically severe pest in Kenya and Tanzania, causing severe defoliation. The attack is often first confined to the lower leaves of a small group of coffee trees. They are most common in hot dry weather. Outbreaks have been associated with injudicious use of pesticides.
What to do:
|
| Coffee berry moth (Prophantis smaragdina) The adult is a small golden brown moth with a wingspan of about 1.3 mm. The female moth lays scale-like eggs singly on or near green berries. The caterpillar is reddish to pink in colour with dark markings on the back, and measures 13 mm when fully grown. Caterpillars bore into green, half-grown berries, starting near the stalk and hollow them out. One caterpillar usually attacks several berries in 1 cluster. Attacked berries turn brown to black. When 1 bean has been eaten, it leaves the berries and wanders over the cluster of berries joining them with threads of silk before boring into a second berry. Flower buds and the tip of suckers may also be attacked. Caterpillars pupate on the ground between dry leaves. Occasionally severe attacks occur at low altitudes. Frequently slight damage by the berry moth is considered beneficial since it has the effect of thinning out overbearing branches.
What to do:
|
| White coffee borer (Anthores leuconotus) Adult beetles of the white coffee borer (also called white stemborer) are about 3 cm long and have very long antenna. They are dark brown greyish in colour; the wing cases are greyish white with dark markings near the end. Adult beetles feed on the bark of branches, causing little damage. Female beetles lay eggs on the trunks of trees usually at the base near the ground level. The whitish, legless larva burrows into the bark and the wood of the trunk and main roots. The larva pupates in a large chamber within the trunk. The attack by larvae causes serious damage, particularly if the trunks are almost ring-barked. Young trees may be killed.
Older trees wilt, turn yellow and produce a poor crop. Symptoms of attack are round exit holes of the adult beetles in the trunk and wood shaving extruding from the bark or from the roots just below soil level. The white borer can become a serious pest especially below 1500 m (5000 ft) on shallow or eroded soil near shade trees.
What to do:
|
| Termites can be a serious problem for coconut palms, particularly for young trees in tree nurseries or trees that have just been transplanted into the field. Termites live in the soil in hills, construct tunnel from the hills to the palms and feed on all parts of young coconut palms. Damage occurs mainly during the dry season.
Many plants have a repellent or even insecticidal effect on termites and can be applied as spray directly against termites or as barrier around the trunk of coconut palms:
What to do:
|
| Red coffee mite (Oligonychus coffeae) The red coffee mite may be a pest of unshaded coffee in localised attacks during the dry season. They attack the upper surface of mature leaves. As a result the upper surface of fully hardened leaves turn a rusty, purple or yellow brown colour. Under drought stress young leaves may also be attacked.
What to do:
|
| Root-knot nematodes (Meloidogyne spp.) Important nematodes attacking both Arabica and Robusta coffee are Meloidogyne arenaria, Meloidogyne decalineata and Meloidogyne incognita, causing root knots and galls. Other nematode species include Pratylenchus coffeae, Radopholus similis, Rotylenchus iperoiguensis and Rotylenchus pararobustus.
Field symptoms are typically of stunted, poorly growing plants with yellowing leaves. Infected root systems show characteristic knots or galls, the severity of which varies with the degree of nematode infection and species and variety of plant parasitized. Strategies of cultural control are less well developed and crop rotations are difficult to design because of the wide host range of Root-knot nematodes. Groundnuts or maize, which are both poor or non-hosts to M. incognita, have been evaluated for use in cropping systems designed to manage this nematode. What to do:
|
| Antestia bugs (Antestiopsis spp) Antestia bugs are major pest of Arabica coffee in East African countries. The adult bug is shield-shaped, about 6 to 8 mm long and strikingly coloured dark brown with orange and white markings. They hide in berry or flower clusters. Females lay eggs in groups of about 12 on the underside of leaves. Newly hatched nymphs are about 1 mm long. Nymphs resemble the adults in colour but have a more rounded shape and lack functional wings.
Both adults and nymphs cause severe damage to green berries by feeding and indirectly by the transmission of a fungus (Nematospora coryli), which causes rotting of beans. The bug also attacks flower buds and shoots causing blackening of flower buds with no flower/fruit set. Attacked branches grow side shoots (fan branching). No visible surface marks / scars or wounds on berry are noticeable until seen on drying beds as "zebra" beans. "Zebra" beans produce poor quality coffee and are possible avenues for fungal infection. Antestia bugs can live on shrubs belonging to the same family as coffee (Rubiaceae family).
What to do:
|
| Capsid bug (Lamprocapsidea (Lygus) coffeae) The capsid bug is a serious pest in all areas. The adult bug is green or brownish and about 0.7-0.8 mm long, and has a sharp downward bent in its wings, which is highly characteristic. Females insert eggs into flower buds, and thus eggs are not visible. Nymphs are pale green and pear shaped. Wing buds are visible on older nymphs. Both adults and nymphs feed on flower buds, but when they are not present they would feed on any soft green part of the coffee bush. As a result of feeding flower buds blacken due to death of stamens and petals. The style however remains healthy and usually takes a club shaped appearance with pale green shaft and black head. Damaged flowers do not set fruit. This bug is frequently considered beneficial on unshaded coffee at lower altitudes since the pruning effect of the damage caused by this bug reduces the tendency to overbear.
What to do:
|
| Leafmining caterpillars (Leucoptera meyricki and Leucoptera caffeina) The adults of leafminers are very small (3-4 mm long) white moths. They lay very small eggs (just visible to the naked eye) on the upper leaf surface scattered in small groups (L. meyricki) or touching each other in a neat row along a main vein (L. caffeina). Upon hatching, the caterpillars bore into the leaf and mine just below the upper leaf surface. The mines of each L. meyricki caterpillar are initially separated but after few days they join to form one large mine. The young caterpillars of L. caffeine produce one communal mine. These mines appear as irregular brown blotches on upper side of leaves, which when opened reveals many whitish caterpillars. Caterpillars are flattened, white and very small (4-8 mm when fully grown). Mature caterpillars come out of the mine and pupate in a H- shaped cocoon (6 mm long) on dead leaves on the ground or on the underside of leaves on the tree. The mining activity causes a reduction of the active leaf surface, reducing assimilation. Attacked leaves are usually shed prematurely. Leafminers can live on shrubs belonging to the same family as coffee (Rubiaceae family).
What to do:
|
| Leaf skeletoniser (Leucoplema dohertyi) The leaf skeletoniser is normally a minor pest but severe outbreaks could occur especially in nurseries.
The adult is a grey and brown moth with a wing-span of about 1.3 cm. It is often found on leaves during the day with the hind wings drawn back alongside of the body and the narrow forewings held at right angles to the body. They lay yellow-green eggs (0.5 mm in diameter) singly or in small groups mainly on the underside of leaves. The caterpillars are greyish white with many pimple-like projections on the body. They turn red the day before pupation. Fully-grown caterpillars are about 8 mm long. They feed on underside of the leaf, usually near the near mid-rib leaving many irregular lace-like patches.
What to do:
|
| Giant looper (Ascotis selenaria reciprocaria) The adult is a moth with a wingspan of up to 5 cm. They vary in colour from dark brown to light grey with numerous dark grey markings. They lay pale green eggs in crevices in the bark. The caterpillars are pale grey to dark brown resembling twigs, and move with a looping motion. They are about 5 cm when fully grown. Young caterpillars usually eat pits on the upper leaf surface and older caterpillars feed on the leaf margins leaving a jagged edge. All stages of caterpillar prefer tender and young leaves but berries and large flower buds may also be attacked. Alternate hosts include groundnuts, sweet potatoes, black jack weeds as well as some tree species like Datura and Eucalyptus.
What to do:
|
| Kenya mealybug (Planococcus kenyae) This mealybug was a major pest of coffee in Kenya in the 20's and 30's in the East Rift area, but it was successfully controlled with introduction of natural enemies from Uganda. Sporadically severe attacks occur especially in the colder months of the year. The mealybugs appear as white masses between clusters of berries and flower buds or sucker tops. They are often attended by ants, which feed on the sticky honeydew excreted by the mealybugs. Honeydew leads to growing of black sooty mould on the upper surfaces of leaves.
What to do:
|
| Root mealybug (Planococcus citri) This mealybug is usually a minor pest of coffee, but it is potentially a serious pest. The mealybugs attack the roots where they usually live in association with a fungus (Polyporus sp.), which forms a crust over the mealybugs. Seedlings and very young trees are often free of the fungus. Attacked trees show wilting yellow leaves as if suffering from moisture stress. When affected trees are uprooted, the roots are stunted and encased in brown fungus. When the fungus is pealed off, the white mealybugs can be seen.
Damage is more prominent in dry conditions. The pest is associated with poorly established coffee. Severe infestation may lead to loss of quality, failure of berries to ripen and overbearing and die-back. Identical mealybugs have been reported on Solanum spp., Combretum spp. and Indigofera spp. The root mealybug is also known as the citrus mealybug. It also attacks citrus and cocoa, where it normally attacks the aerial part of the plants.
In the highlands of Java, the shade tree Leucaena glauca is main food plant of citrus mealybug at altitudes above 600m (2000 ft.). Measures that proved successful for the control of citrus mealybug were mainly directed against infestation of this tree and consisted of removing the flower clusters or, when necessary, pruning all foliage and flowers. It is also claimed that citrus mealybug can be controlled by increasing the shade in plantations and that this was undesirable for Robusta coffee but suitable for Arabica at high altitudes. Good results were obtained by providing three covers, one above the other, of Leucaena, Erythrina and Albizia, or with Leucaena and Albizia only. It is further suggested that because the insect infests mainly the flowers and pods of L. glauca, other shade trees that seldom flower, such as L. pulverulenta (L. leucocephala), or a sterile hybrid of L. glauca and L. glabrosa should be planted. What to do:
|
| Star scale (Asterolecanium coffeae) It is yellowish to reddish brown, covered with numerous small spines. It attacks stems and branches, causing deformation of branches. The growth of trees severely attacked is retarded and the trees may be die. Symptoms include green branches bent at nodes with pits in green bark beneath the bend, drooping dead leaves on affected nodes and numerous small red or yellow objects are found in the bark crevices especially near the ground. Alternative hosts include Jacaranda and loquat trees.
What to do:
|
Information on Diseases
General information
Conventional coffee plantations are generally confronted with many pests and diseases. In practice, on ecological coffee plantations, the following may be of relevance. An infestation of either pests or diseases is always an indication that the coffee eco-system is not balanced, and the causes must be investigated.
Possible causes are:
- The site is not suitable (too low altitude, too warm, too humid, stagnant water, too dry, wrong variety)
- Soils are degenerated and poor, lacking organic material (humus).
- Too little diversity and too few shading trees.
- Not following the correct succession of the forest system, the trees are too old or the wrong variety.
- Varieties too close together, which have an identical status in the system.
- Failure to trim the shading trees (too much shade).
Examples of Coffee Diseases and Organic Control Methods
| Coffea leaf rust (Hemileia vastatrix) It is the major disease in Arabica coffee. Yellow to orange powdery blotches appear on the underside of leaves, chlorotic patches appear on the upper side. They grow from 2-3 mm diameter to several centimetres. On older leaves, several lesions can merge together. This produces irregular diseased areas covering much of the leaf. However, diseased leaves are usually shed before this stage. A major effect of coffee leaf rust is that it causes defoliation. The disease is spread by spores from lesions on the underside of leaves by wind and rain. Under humid conditions, hyper-parasitic fungi such as Verticillium lecanii grow over the lesions, which produces a pale mycelial growth. Leaf rust is favoured by wet, warm weather. Rainstorms of 7.5 mm or more are needed to cause disease outbreak.
What to do:
|
| The coffee berry disease (Colletotrichum kahawae) Colletotrichum kahawae of Arabica coffee only occurs in Africa, and causes major damage in East Africa and Cameroon. Other names of this disease are "coffee berry anthracnose" and "brown blight of coffee". The characteristic symptom is a progressive blackening of young, expanding coffee berries. This begins as small water-soaked lesions. They rapidly become dark and sunken. As they grow they cause the whole berry to rot. Under humid conditions, pink spore masses become visible on the surface of the lesion. Berries often drop from the branch at an early stage of the disease. This is a characteristic feature of coffee berry disease. Lesions may also occur on young berry stalks, causing them to be shed before lesions are visible on the berry itself. The disease also affects ripening berries causing a 'brown blight' phase. This phase is characterised by typical dark, sunken lesions that envelop the red berry. The coffee berry disease may also infect flowers under very wet conditions, and causes brown lesions on petals. This disease does not kill trees, but crop losses can be more than 80%. Spore dispersal within the tree is by rain splash. Disease spread from tree to tree and from farm to farm is by coffee pickers, birds or infected seedlings. Wet conditions and temperatures between 15 and 27.7° C favour disease development. What to do:
|
| Armillaria root rot (Armillaria heimii) Symptoms include wilting of leaves, death of verticals and subsequent death of affected trees. The root system of affected trees shows a white growth (mycelial) of the fungus beneath the bark. In advanced stage of the disease the wood of the affected tree is decomposed into a white, wet mass with characteristic black zone lines running through the wood tissue. Vertical cracks may occur at the base of the stem at this stage. Initial infection in coffee plantings usually can be traced to shade trees or woody debris (stumps or old roots of shade trees) left in the ground when land is cleared before coffee planting.
What to do:
|
| Coffee wilt (Fusarium xylarioides) Indicative symptoms include wilting, chlorosis and defoliation of the aerial parts of the crop, and numerous vertical and spiral cracks in the bark of the trunk. Inspection under the bark, especially around the collar, will reveal characteristic blue-black streaks in the wood. Fungal fruiting bodies (stromata) producing spores can be observed in the bark. Infected berries turn red and appear to ripen early. Seed infection causes blue-black discolouration of the parchment and silver skin. Spores are spread by wind, rain and through human activities (harvesting, pruning etc.). The pathogen can penetrate through wounds so any agency causing wounds will aid the spread of the fungus. Insects may also spread the disease from tree to tree.
Seed from infected berries may contain the pathogen and seed-borne infection is one way in which the disease is spread. Seedborne infection is responsible for seedling blight where the cotyledons fail to unfold, the stem becomes necrotic and the seedling dies. Infected seedlings often survive the nursery stage and later develop collar rot.
The fungus is soil-inhabiting and can penetrate through wounds in the aerial parts or superficial roots. The incubation period from first symptoms to death of the tree varies from days in young plants to 8 months in trees more than 10 years old, although most affected trees die 2-3 months after initial symptoms are observed.
What to do:
|
| Damping-off diseases (Rhizoctonia solani and Pythium spp.) Damping-off affects coffee-seedlings in nurseries. It is caused by a complex of soil-inhabiting fungi such as Rhizoctonia solani and Pythium spp. It should not be a problem in well-maintained coffee nurseries. Factors that predispose plants to attack include over watering, over shading and acid soil.
What to do:
|
| Bacterial blight of coffee (Pseudomonas syringae pv. garcae) Bacterial blight of coffee (BBC) is confined to a few coffee growing areas in Kenya (Solai in Nakuru District and around Mt. Elgon). Recently a few cases have been reported in the East of Rift Valley.
This bacterium is favoured by cool wet weather. Lesions appear on leaves with water soaked margins at start of infection. Leaves eventually dry up and roll inwards turning brown. Dead and dried leaves do not shed but remain attached to the plant. Symptoms occur on secondary or tertiary branches and in severe cases the heads may be affected. On twigs the terminal bud is attacked. Infection then extends downwards, resulting in dieback. Flowers and pin-heads shrivel and turn black.
The initial symptom is the blackening of a node often accompanied by blackening of the petiole and basal part of the leaf. This leads to death of the branch above the node and leaves on the branch turn brown and eventually necrotic (burnt). Severely affected trees appear scorched as if by fire. The bacterium persists on leaves, berries and on green and matured bark. During cool, wet weather, the bacterium multiplies and initiates an epidemic. The entire crop may be lost.
What to do:
|
| Fusarium Bark Disease (Fusarium stilboides) Not widely spread in Kenya except in Taita Taveta District and Makuyu area in Eastern Province. It occurs in 3 different forms and not necessarily all forms present at the same time:
1. Storey's Bark Disease (most common). Suckers attacked at base causing depressed dark brown lesions with yellow margins at times. Pink spore masses are sometimes seen on lesions, which girdle the stem. Girdled old suckers at times continue growing with constriction of bottle neck at base. Weakened suckers may break from wind or picking.
2. Scaly bark (second most common). Bark of the tree rises up in flakes on mature stems. Cankerous regions may develop and die back can follow, though affected stems could also survive.
3. Collar rot. Infection spreads downwards from infected suckers, gradually girdling the tree base. Cankerous lesions develop round stem base at soil level. Constriction appearance may occur and die-back begin from top of tree. Mulching too close to the stem may cause similar rot. Soil- borne fungi may cause seedlings in the nursery to die in the same manner.
What to do:
|
| Fusarium Root Disease (Fusarium solani) This fungus may stay in the stem and roots for years without symptoms until whole tree suddenly dies. The fungus enters through wounds on roots caused by ploughing, herbicides, die-back, frost or water logging. Symptoms appear when tree is subjected to water stress. If stem is cut near soil level, a purplish pink stain is seen. Dry rot will also show at centre of wood if infection has stayed long. This disease does not spread from tree to tree.
What to do:
|
Information Source Links
- Bohlen, E. (1973). Crop pests in Tanzania and their control. Bfe. Federal Agency for Economic Cooperation.
- CAB International (2005). Crop Protection Compendium, 2005 Edition. www.cabi.org Wallingford, UK
- Coffee organic cultivation, 2000, Naturland. Available also online www.naturland.de
- Coffee Research Foundation. Document on Coffee Arabica. www.crf.co.ke
- Coffee Research Institute www.coffeeresearch.org
- Coffee Research Station (1989). An Atlas of Coffee Pests and Diseases. Published by the Coffee Research Foundation. Third Revision. Kenya.
- Depieri, R. A. , Martinez, S.S. and Menezes Jr, A.O. (2005). Compatibility of the fungus Beauveria bassiana (Bals.) Vuill. (Deuteromycetes) with extracts of neem seeds and leaves and the emulsible oil. Neotropical Entomology. vol.34 no.4. Print ISSN 1519-566X
- EcoPort www.ecoport.org
- Hill, D. (1983). Agricultural insect pests of the tropics and their control. 2nd Edition. Cambridge University Press. ISBN: 0-521-24638-5
- Mahdi, H.S., Al Hakimi, A., Mahyoub, M, Sayef, A., Al Sharjabi, S., and Pola, F. (2006). Traditional methods of integrated pest management are a promising strategy to reduce population density of coffee berry moth prophantis smaragdina (Butler) in the field. Ninth Arab Congress of Plant Protection, 19-23 November 2006, Damascus, Syria. www.asplantprotection.org
- Nutrition Data www.nutritiondata.com.
- OISAT. Organisation for Non-Chemical Pest Management in the Tropics. www.oisat.org
- Republic of Kenya: Economic Review of Agriculture2006
- Smith, L. and Bellotti, A. C. (1996). Successful Biocontrol Projects with Emphasis on the Neotropics. Cornell University. Conference in Biological control. April 1-13, 1996.
Contacts
- Coffee Research Foundation, P.O.Box 4, 00232 Ruiru, Kenya Tel: +254: (20) 2176420, 2176427, 0733 333 060/ 0724 527 611
Email: director.cri@kalro.org